What can we do to eliminate the risk of the targeted attacks? Obviously, we need to implement some kind of technical solution, which would combine the best ideas in the field of unknown threats detection. However, before talking about the solution, let’s try to understand the nature and the meaning of the “targeted attack,” as well as key principles of an offensive operation.
These days news is filled with similar stories: “As a result of a targeted attack, criminals managed to steal $2 billion from the accounts of 40 banks and financial companies all over the world,” “More than 500 industrial companies working in the fields of construction and metal manufacturing from more than 50 countries all over the world, became victims of a well-planned targeted attack,” “Highly efficient and properly installed malicious software intended to attack the SWIFT system, allowed cybercriminals to steal millions…” and many other similar topics and discussions.
The targeted attacks or so-called APTs are one of the biggest problems of the modern era, and there are many multimillion companies working in the field of their elimination. While trying to visit a cybersecurity expo, we will definitely see the following things: APT is important for sellers, who need to include it into their offer, and for buyers, who have to deal with this problem. At the same time, targeted attacks became incredibly important not only for the giant corporations but even for the companies working in the field of medium and small business. If an attacker wants to reach the assets of a corporation, they could use one of the contractors as a pivot point for their attack.
Not just scary words
Unfortunately, such term as “targeted attack” are not really correct. Why? Let’s think about the initial meaning of a cyberattack: “A cyberattack is any type of offensive maneuver that targets computer information systems…” Stop right now! Even these words are more than enough. As you can see, any attack targets an object.
The key difference of the targeted attack is the fact that the attacker implements an active and intelligent approach to the process of the Key Intelligence Topics specification, entry-points selection, thoroughly analyzing the information circulating within the target network, and using collected data in order to gain access to the most precious assets.
Someone may not agree with me saying the following: “People lose their money, while you are trying to catch the words!” At the same time, the academic precision in the process of the problem description is incredibly important to create the long-awaited “silver bullet”.
In the majority of cases, experts are trying to work with independent components of the targeted attack without thinking about the complexity of the problems. As a result, all available ways of such threats detection and remediation are not reliable and can’t be used in the affected network.
For example, many security measures are based on the static lists of templates, i.e. the databases for the heuristic analysis, white lists, signature and so on. At the same time, such a list is useless for new TTPs, when attackers try to hide their presence within the affected infrastructure.
To create a method that would correspond with a huge variety of requirements of continuously changing threat landscape, we need to develop reliable trusted environments. According to the “paper security” requirements, this is the only way to protect the information during all stages of its processing.
Unfortunately, this method is not really efficient from a practical point of view. Modern IT-environments are usually built using hardware and software from different vendors, who use totally different approaches and solutions during the process of development, as well as unique update and support technologies. It’s simply impossible to assess all the products in order to find malicious implants and vulnerabilities, while a trusted environment can’t be built without doing this.
Another option that allows protecting important assets from targeted unauthorized access is based on the principle of the physical isolation of the protected objects. At the same time, it’s not an effective solution in the conditions of real life. Even if one is able to block all the additional communication channels, which could be used by adversaries in order to gain access to the data, you can’t eliminate the human factor. In many cases, such additional communication channels are created by legitimate actors working with the system. Their action can be performed unintentionally as well as knowingly planned.
The problem of finding a solution
It turns out that it’s virtually impossible to eliminate the risk of unauthorized access to the information. As a result, we need to implement solutions, which would allow discovering unknown types of attacks within the compromised environment. This type of solutions is proudly called the post-breach one and intended to solve the response/mitigation issue in the majority of cases in order to react and mitigate the threats.
It’s worth noting that there are almost no post-breach detection solutions, which allow identifying the threats in a timely manner. For example, one of them represents the network of traps called ‘honeypots’.
A properly implemented trap can really help to detect and contain a targeted attack on its active stage. At the same time, the classic version of the honeypot won’t be able to identify other points of presence of the attacker.
There are several ways of the flexible trap system expanding, as well as methods of detailed system component operation analysis, which allow detecting anomaly within the network. It’s really hard to find detailed recommendations, how to choose the correct parameters of honeypots implementation in the production environment. How many fake workstations should be deployed within the network? Which fake accounts should be created and on which endpoints? The correct processing of the data is even harder than the data collection. “Okay, Google! Someone used fake credentials on the workstation of our accountant. What should we do now?”
Unknown ≠ Supernatural
In order to avoid misunderstanding of terms, we are going to use the “unknown cyberattack” term. It can include features of the targeted attacks, but it won’t be limited only to them. The unknown cyberattack is a continuous, intentional, and unauthorized operation in target infrastructure with the operational parameters that cannot be detected real-time with a standard set of security rules.
Does it sound too complex? In fact, the attacks the three distinctive features: it’s continuous, targeted (no, Captain, I mean the attacker has Key Intelligence Topics related to the attack object), and non-trivial (for detection mechanism).
The continuity is the feature that defines the time range, when the attacker has access to the asset, or he’s still able to affect it. In particular, the targeted attacks always involve continuous control of pivot points in the affected information system.
The targeted character is a feature that defines the volume of manual operations of the attacker in order to gain unauthorized access or affect the asset. Such actions always depend on the specific features of the target.
The non-trivial character of the attack is the feature that defines the complexity of the process of the attack detection by security mechanisms of the attacked infrastructure. It’s directly connected with the targeted character of the attack. This is the key feature that is used to assess the level of efficiency of security systems and methods.
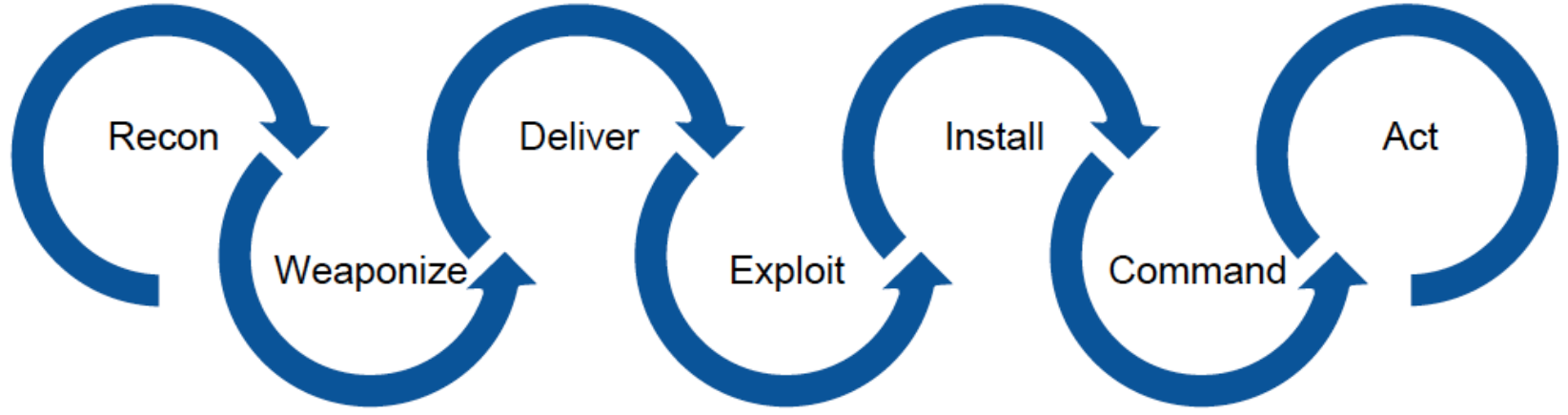
The life-cycle of the attack
Any cyberattack can be divided into several stages. The names of these stages were taken from the military field. Each stage of the attack includes a specific set of TTPs to perform it. There are different preventive measures and counter-strategies for each of the stages.

Let’s make real examples to understand each of the stages of the attack life-cycle and discuss the mitigation strategies for each of them.
We need to remember that these examples are just particular cases from a huge variety of TTPs, which can be performed by the attacker.
Intelligence and preparation
During the intelligence stage, the attacker is trying to find the entry points to the victim’s infrastructure. For example, to perform it, he needs to assess the detailed report of their vulnerability scanner that was used to analyze the publicly available application on the victim’s perimeter.
Furthermore, the attacker can use the results of various search engines in order to define the list of exploitable resources with the IP addresses within the range of the target company.
Imagine that attacker found social profiles of several employees of the target company, as well as their corporate emails. By using the obtained information, the attacker prepared the following plan of action.
Make an attempt to gain access to the corporate workstations of the mentioned employees.
In case of failure, the attacker will try to use public exploits in order to attack the servers of the company connected to the Internet, as well as Wi-Fi routers installed in the office of the company.
At the same time, simultaneously with the first two actions, the attacker will try to find vulnerabilities in the public web app in order to discover a way to gain access to the internal infrastructure via the app.
In order to implement all the stages, the attacker will prepare an email with malicious software to send to the employees. The attacker will customize discovered exploits and start the process of a brute-force password attack against the web app.
Delivery, exploitation, and gaining positions
Which of the possible entry points has the highest chance for success? One person might say that the web app is the most valuable and vulnerable component for the initial stage of an attack. Someone else might think about the human factor and low security awareness of the employees. In this case, someone would say that the most effective method is spear-phishing emails.
At the same time, attackers don’t really care about your opinion. They are already in the office of the company with their laptop, waiting for the devices of the employees. As a result, the attacker is able to reach their goals at this stage: the malicious code will exfiltrate the sensitive information to the controlling server of the attacker.
Action
This is the most interesting stage of the entire process. In real life conditions, the attacker needs to perform a lot of additional actions in order to create new pivot points and reach the highest level of persistence. They need to perform a proper internal reconnaissance to analyze the compromised structure and to find a way to reach the most valuable resources. This process is called lateral movement: there is almost no chance that the infected computer of the accountant will satisfy the needs of the attackers because they are more interested in gaining access to the intellectual property of the company. Don’t forget that the attacker needs to perform the proper exfiltration of the obtained information at the stage of the attack.
Countermeasures
There is no doubt that active countermeasures should be implemented Blue Team before all of the aforementioned stages. However, sometimes people start searching for their adversary only after he has already left the network with sensitive data. In the majority of cases, it happens as a result of the low qualifications of the defenders. The thing is the adversary had a lot of time to analyze the behavior of their victim before the active stage of an attack. He never performed any actions before understanding the victim’s security posture and all the security measures in place. At the same time, there are always a huge number of attackers, while some of them will be hidden among the employees of the company.
Basing on the ideas mentioned above, we need to learn everything about the attacker and his actions even before the moment when they start to implement the first stages of his attack. In order to succeed at this, we need to learn how to detect the early activities of the attacker in the corporate infrastructure. I will tell more about the entire process in my next post.